finally the FP is over..and this is our report..
the file is in pdf format and we also have the tutorial for FP 7 in video(i'll post it later)..
here is the link:
Discrete Math report
Selasa, 22 Desember 2009
Minggu, 20 Desember 2009
7th Task
hi friends!!! xD
after long time, finally we've did our 7th task...
this task is about expert system in prolog..
you already read our idea for expert sysytem, didn't you?
our idea for expert system is type of haircut and glasses for some shape of our face, such as oval, square, oblong, triangular and round...
these are the tutorial....
after long time, finally we've did our 7th task...
this task is about expert system in prolog..
you already read our idea for expert sysytem, didn't you?
our idea for expert system is type of haircut and glasses for some shape of our face, such as oval, square, oblong, triangular and round...
these are the tutorial....
- first make a notepad then write down the formula for expert system..this is our formula
- then write down the shape of your face(oval,square,oblong,triangular or round)..
- give a full stop(.) after you write down the type of your face. Then 'ENTER'
- you will get the result..and this is the example of the result...
Rabu, 09 Desember 2009
6th task
We’ll find who’s the professor from people who listed here and have another job. We will find the professor using looping function of prolog programme
- Make a new notepad and then write down the input and formula(look at the first picture).
- Saving file under the name prof.pl
- Consult the file on plwin then write find then ‘ENTER’.
- Look at the result at second picture!
6th task
The second excerise is the looping function that made the programme loop every word we typed.
- Make a new notepad and write the formula(look at the first picture).
- Save as under the name go.pl
- Then consult go.pl in plwin then write go. Then ‘ENTER’.
- Now write a word give full stop behind the word (.), then ‘ENTER’.
6th task
Loops in prolog programme
- We will make a looping to get know about the square of some number
- Make a new notepad file then write the formula(look at the first picture).
- Save file under the name loop1.pl
- Now open loop1.pl, then write down outsquare(4,9)* then ‘ENTER’. You’ll see the result like this. We’ll see the result of squared from number 3until number 10 (we just need to write the command once and then the result will be looping if the condition is true )
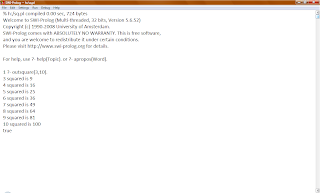
P.S
(4,9) : Actually you may write another number, but make sure that the first number is lower than second number.^^
Selasa, 08 Desember 2009
Resume bab 6
Label:
FP6
RESUME
6.1 LOOPING A FIXED NUMBER OF TIMES
Loops enable a set of instructions to be executed a fixed
number of times. In prolog, looping can be obtained using recursion. In this
case, looping function on PROLOG is similiar to another programming language.
We can see in the example given below:
loop(0).
loop(N):-N>0,write('The
value is: '),write(N),nl,
M is N-1,loop(M).
Those clauses means that ‘the terminating condition of the recurtion
is 0. To loop from N, first determine the value of N, then substract it to
having M, then loop from M, until the value is 0. If the value is 0, the
looping process is stopped there’
6.2 LOOPING UNTIL A CONDITION IS SATISFIED
No facility on PROLOG that directly enable
a set of
instructions to be executed repeatedly until a given condition is met. But there are two way to
obtained the similiar effect :
-
Recursion
Recursion read the input from
keyboard, and output it to the screen, until the ‘end’ instruction is
endountered.
Example of the form :
go:-loop(start). /* start is a dummy value used
to get
the
looping process started.*/
loop(end).
loop(X):-X\=end,write('Type
end to end'),read(Word),
write('Input was '),write(Word),nl,loop(Word).
The last clauses mean: The looping of
X will be stopped if the ‘end’ is encountered. Saat looping berlangsung (before
‘end’ had encountered), PROLOG will always ask the user to enter the input by
the sentence ‘Type end to end’ .
-
Using the ‘repeat’ Predicate
The goal repeat doesn’t repeat
anything, it will be succeeds whenever it’s being called. If user enter another
term but yes or no, PROLOG will always repeat the instruction until the user
enter the term ‘yes’ or ‘no’. This is the example of the form :
get_answer(Ans):-
write('Enter
answer to question'),nl,
repeat,write('answer
yes or no'),read(Ans),
valid(Ans),write('Answer
is '),write(Ans),nl.
valid(yes).
valid(no).
In the case of looping, the two goals write(‘answer yes or no’) and read(Ans) will
always repeat until the condition valid(Ans) had satisfied.
Repeat predicate can also processing
the sequence of terms from a specified file an outputs them until the term
‘end’ is encountered.
The example of the form :
readterms(Infile):-
seeing(S),see(Infile),
repeat,read(X),write(X),nl,X=end,
seen,see(user).
Then, the file that will being
outputted containing (for example, the file ‘myfile.txt’ :
'first term'. 'second term'.
'third term'. 'fourth term'.
'fifth term'. 'sixth term'.
'seventh term'.
'eighth term'.
end.
Then, call the goal readterms will
produced a result :
?- readterms('myfile.txt').
first term
second term
third term
fourth term
fifth term
sixth term
seventh term
eighth term
end
yes
If ‘end’ hasn’t been encountered,
there will be a looping process between the goals repeat and X=end.
6.3 BACKTRACKING WITH FAILURE
This chapter
describes how a set of goals can be evaluated repeatedly in Prolog,
either a fixed
number of times or until a specified condition is met, and how
multiple
solutions can be arrived at using the technique of 'backtracking with
failure'.
Langganan:
Komentar (Atom)







